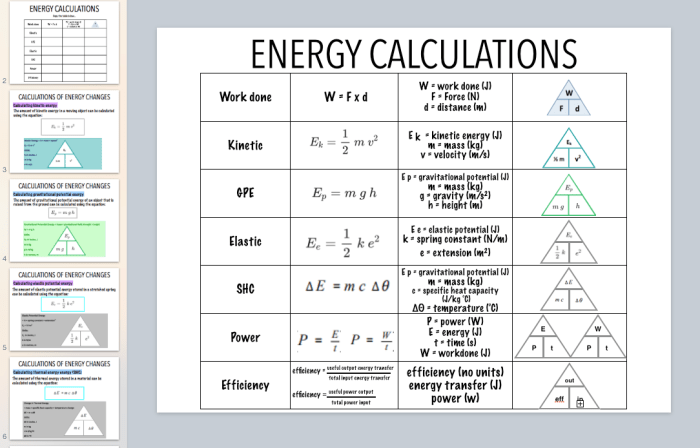
Electrical Code Calculations Level 1 Lesson 4 delves into the intricate world of electrical systems, providing a comprehensive understanding of conductors, overcurrent protection, branch circuits, grounding and bonding, service calculations, and transformers. This lesson empowers learners with the knowledge and skills to navigate the complexities of electrical code calculations, ensuring safety and efficiency in electrical installations.
The journey begins with an exploration of conductors, the vital components responsible for carrying electrical current. Learners will delve into the concept of overcurrent protection, a crucial safeguard against electrical hazards. Various types of overcurrent protective devices will be examined, highlighting their roles in preventing damage to electrical systems.
Electrical Code Calculations Level 1 Lesson 4 Overview
Lesson 4 of Electrical Code Calculations Level 1 provides a comprehensive overview of fundamental concepts and calculations related to electrical systems. It covers essential topics such as conductors, overcurrent protection, branch circuits, grounding and bonding, service calculations, and transformers.
Conductors and Overcurrent Protection
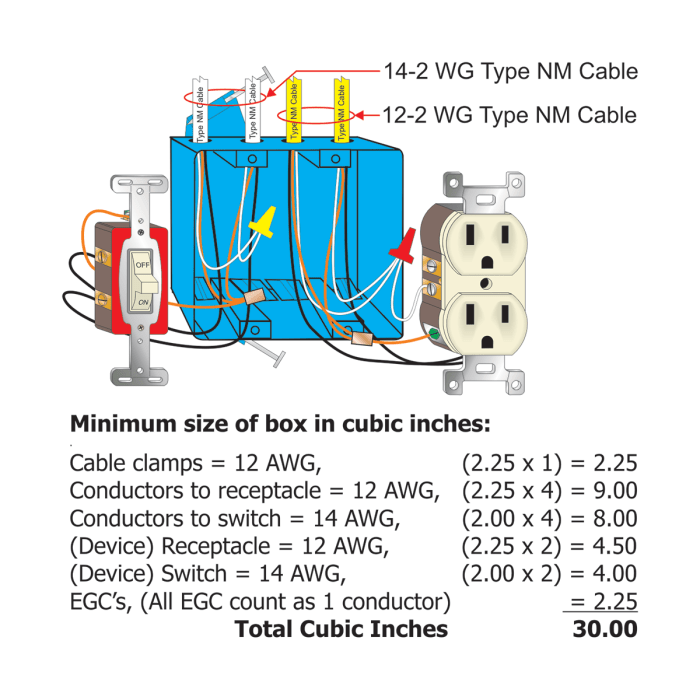
Conductors are the pathways through which electricity flows in an electrical system. Common types of conductors include copper and aluminum wires. Overcurrent protection is crucial to prevent damage to electrical components and fires. Overcurrent protective devices, such as fuses and circuit breakers, interrupt the flow of current when it exceeds a predetermined safe level.
Branch Circuits, Electrical code calculations level 1 lesson 4
Branch circuits are the final distribution pathways of electricity to loads in a building. They are typically sized based on the load they will serve. Different types of branch circuits include general-purpose circuits, lighting circuits, and appliance circuits.
Grounding and Bonding
Grounding and bonding are essential for safety and proper functioning of electrical systems. Grounding provides a low-resistance path for fault currents, while bonding connects various components to the grounding system to prevent voltage differences and ensure equipment protection.
Service Calculations
Service calculations determine the size of the electrical service required for a building. They consider factors such as the total connected load, demand factors, and voltage drop. Accurate service calculations ensure adequate power supply and prevent overloading.
Transformers
Transformers are devices that transfer electrical energy from one circuit to another through electromagnetic induction. They can increase or decrease voltage levels, enabling efficient power distribution and utilization.
FAQ: Electrical Code Calculations Level 1 Lesson 4
What is the purpose of overcurrent protection?
Overcurrent protection is crucial to prevent electrical hazards by interrupting the flow of excessive current that can damage electrical components and cause fires.
What are the different types of branch circuits?
Branch circuits are classified into various types based on their intended use, such as lighting circuits, receptacle circuits, and appliance circuits.
Why is grounding and bonding important in electrical systems?
Grounding and bonding provide a safe path for fault currents to flow, reducing the risk of electrical shock and protecting equipment from damage.