Unveiling the intricacies of the integumentary system, this comprehensive guide, available as an accessible integumentary system worksheet answers PDF, embarks on an enlightening journey through the layers of the skin, unraveling the functions, structures, and disorders that define this remarkable system.
Delving into the depths of dermatology, this guide unveils the diverse roles of skin cells, hair, nails, and sweat glands, while illuminating the significance of the dermis and epidermis in maintaining the health and integrity of our largest organ.
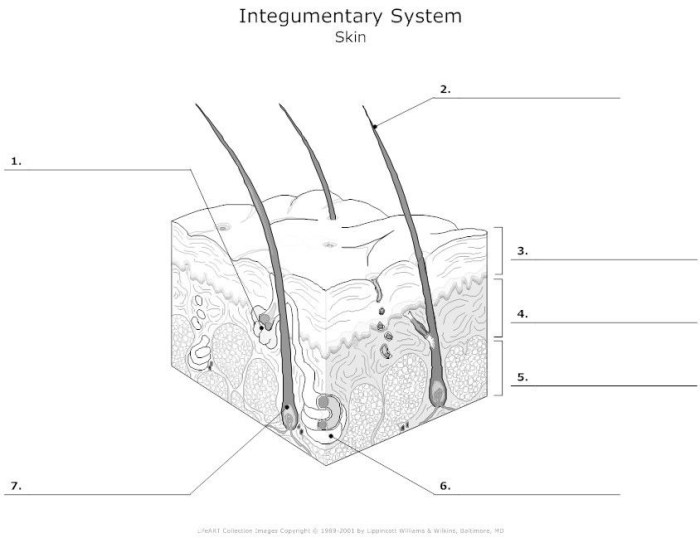
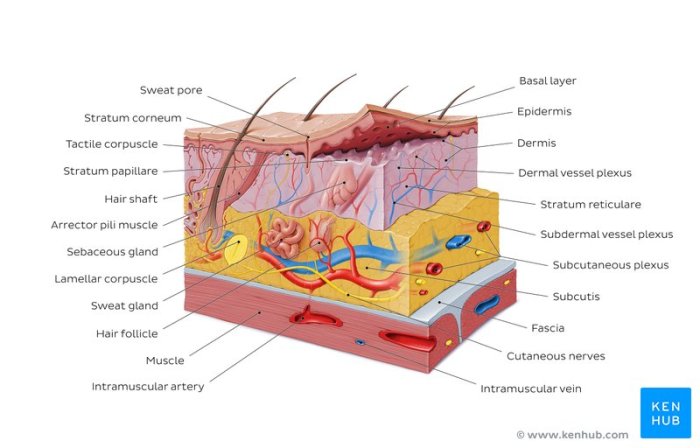
Integumentary System Overview
The integumentary system is the outermost layer of the body, composed of the skin, hair, nails, and sweat glands. It plays a crucial role in protecting the body from external threats, regulating temperature, and facilitating sensory perception.
The skin, the primary component of the integumentary system, consists of three main layers: the epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis. The epidermis, the outermost layer, is made up of keratinized cells that provide a waterproof barrier against pathogens and environmental damage.
The dermis, located beneath the epidermis, contains connective tissue, blood vessels, and nerves. It provides structural support, elasticity, and nourishment to the skin. The hypodermis, the deepest layer, is composed of fat cells that insulate the body and provide cushioning.
Layers of the Skin
| Layer | Description |
|---|---|
| Epidermis | Outermost layer, composed of keratinized cells; provides a waterproof barrier. |
| Dermis | Middle layer, containing connective tissue, blood vessels, and nerves; provides structural support and nourishment. |
| Hypodermis | Deepest layer, composed of fat cells; insulates the body and provides cushioning. |
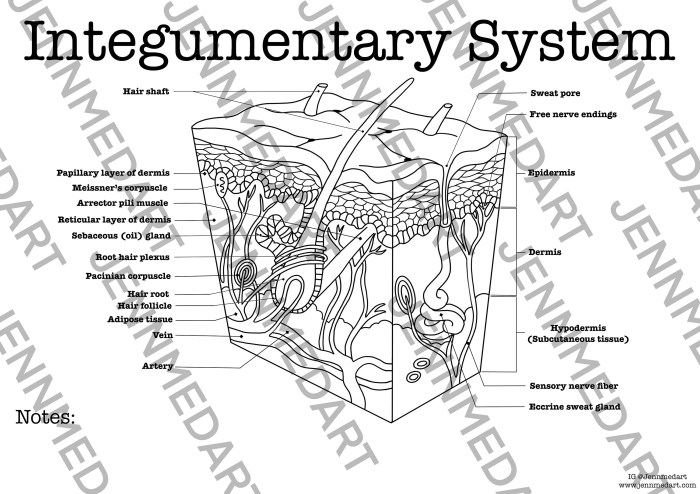
Skin Structures and Appendages
The skin contains various types of cells, including keratinocytes, melanocytes, and Langerhans cells. Keratinocytes produce keratin, a protein that forms the protective outer layer of the skin. Melanocytes produce melanin, a pigment that gives skin its color and protects it from ultraviolet radiation.
Skin appendages, such as hair, nails, and sweat glands, perform specific functions. Hair provides insulation and protection from the sun and cold. Nails protect the tips of the fingers and toes. Sweat glands release sweat to regulate body temperature.
Structure and Function of the Dermis and Epidermis
The dermis is composed of collagen and elastin fibers, which provide strength and elasticity to the skin. It also contains blood vessels that nourish the skin and hair follicles, which produce hair.
The epidermis, the outermost layer, is composed of several layers of cells. The outermost layer, the stratum corneum, consists of dead, keratinized cells that provide a waterproof barrier.
Integumentary System Disorders
Common skin disorders include acne, eczema, and psoriasis. Acne is a condition caused by inflammation of the sebaceous glands, leading to the formation of pimples. Eczema is a chronic inflammatory condition that causes dry, itchy skin. Psoriasis is an autoimmune disorder that causes red, scaly patches on the skin.
The causes of skin disorders vary, but they can be influenced by genetics, environmental factors, and lifestyle choices. Treatment options depend on the specific disorder and may include topical medications, antibiotics, or phototherapy.
Impact of Skin Disorders on Overall Health, Integumentary system worksheet answers pdf
Skin disorders can have a significant impact on overall health, both physically and psychologically. Severe skin conditions can cause pain, discomfort, and itching, leading to sleep disturbances and decreased quality of life.
Additionally, skin disorders can affect self-esteem and social interactions, as they can be visible and stigmatizing.
Integumentary System Hygiene and Care
Proper skin care and hygiene are essential for maintaining healthy skin. Regular bathing or showering with mild soap removes dirt and bacteria. Moisturizing helps keep the skin hydrated and prevents dryness.
Sun protection is crucial for preventing skin cancer and premature aging. Sunscreen with a broad-spectrum SPF of 30 or higher should be applied daily, even on cloudy days.
Role of Nutrition in Maintaining Healthy Skin
A healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains provides the nutrients necessary for healthy skin. Vitamin C is essential for collagen production, while vitamin A promotes cell growth and repair.
Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish and nuts, have anti-inflammatory properties that can benefit skin health.
Integumentary System in Different Animals: Integumentary System Worksheet Answers Pdf
The integumentary systems of different animals vary depending on their environment and lifestyle. Aquatic animals, such as fish, have scales that protect them from water and provide buoyancy.
Mammals have fur or hair that insulates them from cold temperatures. Reptiles have scales that protect them from dehydration and provide camouflage.
Adaptations of Skin and Appendages in Various Species
Skin and appendages have evolved to adapt to specific environments and behaviors. For example, desert animals have thick, leathery skin that prevents water loss.
Nocturnal animals have sensitive eyes and ears to navigate in low-light conditions. Birds have feathers that provide insulation and enable flight.
Role of the Integumentary System in Thermoregulation and Protection
The integumentary system plays a crucial role in thermoregulation. Mammals have sweat glands that release sweat to cool the body. Birds have feathers that trap air to insulate the body.
The integumentary system also protects the body from external threats. The skin’s barrier function prevents pathogens from entering the body. Fur or hair provides protection from predators and environmental hazards.
FAQ Corner
What are the primary functions of the integumentary system?
Protection, thermoregulation, sensation, excretion, and vitamin D synthesis.
Name the three layers of the skin.
Epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis.
What is the most common skin disorder?
Acne.