Select the true statements concerning echinoderms and embark on a journey into the fascinating world of these marine invertebrates. Echinoderms, with their distinctive pentaradial symmetry and water vascular system, exhibit remarkable diversity, ecological significance, and cultural importance. This comprehensive guide unravels the complexities of echinoderms, providing insights into their locomotion, feeding mechanisms, reproduction, and their impact on marine ecosystems.
Echinoderms: Defining Features and Diversity
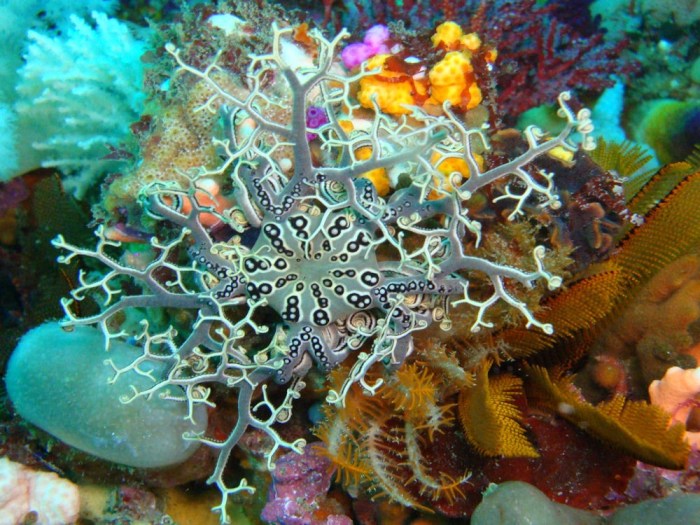

Echinoderms are a unique and diverse group of marine invertebrates that possess distinctive characteristics. They exhibit pentaradial symmetry, with their body parts arranged in multiples of five around a central axis. Their defining feature is the water vascular system, a complex network of fluid-filled canals that serves various functions, including locomotion, feeding, and respiration.
Echinoderms are classified into five main classes based on their body forms and adaptations:
- Asteroidea (starfish)
- Echinoidea (sea urchins)
- Crinoidea (sea lilies and feather stars)
- Holothuroidea (sea cucumbers)
- Ophiuroidea (brittle stars)
Locomotion and Feeding in Echinoderms: Select The True Statements Concerning Echinoderms
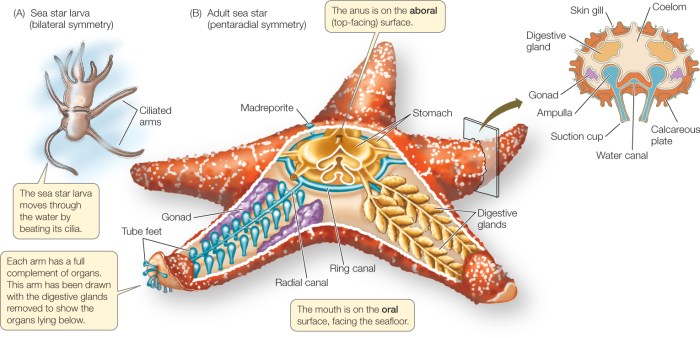
Locomotion
Echinoderms exhibit various methods of locomotion depending on their body structure. Starfish use their tube feet, powered by the water vascular system, to grip surfaces and move. Sea urchins utilize their spines for traction and slow movement. Sea cucumbers contract and expand their muscular bodies to crawl along the seafloor.
Feeding
Echinoderms employ specialized structures for capturing and ingesting prey. Starfish extend their tube feet to capture and transport food to their mouth. Sea urchins use their Aristotle’s lantern, a complex jaw apparatus, to scrape algae from surfaces. Sea cucumbers are filter feeders, using their tentacles to capture suspended particles.
Reproduction and Development in Echinoderms

Echinoderms exhibit diverse reproductive strategies. Some species reproduce sexually, releasing gametes into the water for external fertilization. Others engage in asexual reproduction, such as starfish, which can regenerate entire individuals from a single arm.
Echinoderms undergo unique larval stages during their development. The free-swimming larvae, known as echinoplutei, disperse and feed in the water column before undergoing metamorphosis into their adult form.
Ecological Importance of Echinoderms
Echinoderms play crucial roles in marine ecosystems.
Predation and Herbivory
Starfish are voracious predators, feeding on mollusks, crustaceans, and other invertebrates. Sea urchins graze on algae, helping to control algal growth and maintain the balance of marine habitats.
Detritivores, Select the true statements concerning echinoderms
Sea cucumbers and brittle stars act as detritivores, feeding on decaying organic matter and helping to recycle nutrients in the ecosystem.
Economic and Cultural Significance of Echinoderms
Echinoderms have significant economic value, particularly in the seafood industry. Sea urchins and sea cucumbers are highly prized as delicacies in many cultures. Starfish and brittle stars are often used in aquarium displays.
Echinoderms also hold cultural significance in various societies. Sea stars have been used as symbols of guidance and protection in Native American cultures. Sea urchins are used in traditional Chinese medicine and as ornaments in jewelry.
FAQ Guide
What are the defining characteristics of echinoderms?
Echinoderms are characterized by their unique pentaradial symmetry, a water vascular system, and a calcareous endoskeleton composed of ossicles.
How do echinoderms move?
Echinoderms employ tube feet and podia for locomotion, using hydraulic pressure to extend and retract these structures.
What is the ecological importance of echinoderms?
Echinoderms play vital roles as predators, herbivores, and detritivores, contributing to nutrient cycling and ecosystem balance in marine environments.